SLIDES : Here >>>
Challenges of Securing Information
- Securing information isn’t easy.
- There’s no one-size-fits-all solution.
- We face a huge variety of attack types, and defending against them is often very difficult.
Biggest Cyber Attacks in History
- The Melissa Virus
- NASA Cyber Attack
- The 2007 Estonia Cyber Attack
- A Cyber Attack on Sony’s PlayStation Network
- Adobe Cyber Attack
- The 2014 Cyber Attack on Yahoo
- Ukraine’s Power Grid Attack
- 2017 WannaCry Reandomsware Cyber Attack
- A Cyber Attack on Marriott Hotels went unnoticed for years
- The biggest password leak yet
Difficulties in Defending Against Attacks
- These slides list the challenges faced by defenders:
- increasingly connected devices
- faster and more sophisticated attacks
- readily available attack tools
- rapid vulnerability discovery
- delays in security update
- weak update distribution
- distributed attacks
- the rise of BYOD (Bring Your Own Device), and user confusion.
- These obstacles make defending against attacks significantly harder.
What Is Information Security?
- Core Goal: Protecting digitally stored, manipulated, and transmitted information.
- CIA Triad: Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability.
- Confidentiality
- Ensuring that information is only accessible to those who have been authorized to view it.
- Integrity
- Ensuring that information is correct, accurate, and has not been tampered with.
- Availability
- Ensuring that information and resources are available to authorized users when needed.
- Confidentiality
- AAA: Authentication, Authorization, Accounting.
- Components: Hardware, software, communications, products, people, policies.
Information Security Terminology
- Asset: Anything of value.
- Threat: Potential harm.
- Threat Agent: Source of the threat.
- Vulnerability: System weakness.
- Threat Vector: How the attack happens.
- Threat Likelihood: Probability of an attack.
- Risk: Exposure to danger.
- Risk Management: Avoidance, acceptance, mitigation, deterrence, transference.
Who Are the Attackers?
- Hackers: Black hat, white hat, gray hat.
- Cybercriminals: Financially motivated.
- Script Kiddies: Use readily available tools.
- Brokers: Sell vulnerabilities.
- Insiders: Malicious employees.
- Cyberterrorists: Ideologically motivated.
- Hacktivists: Politically or socially motivated.
- State-Sponsored Attackers: Government-backed.
Attacks and Defenses; Steps of an Attack (Cyber Kill Chain)
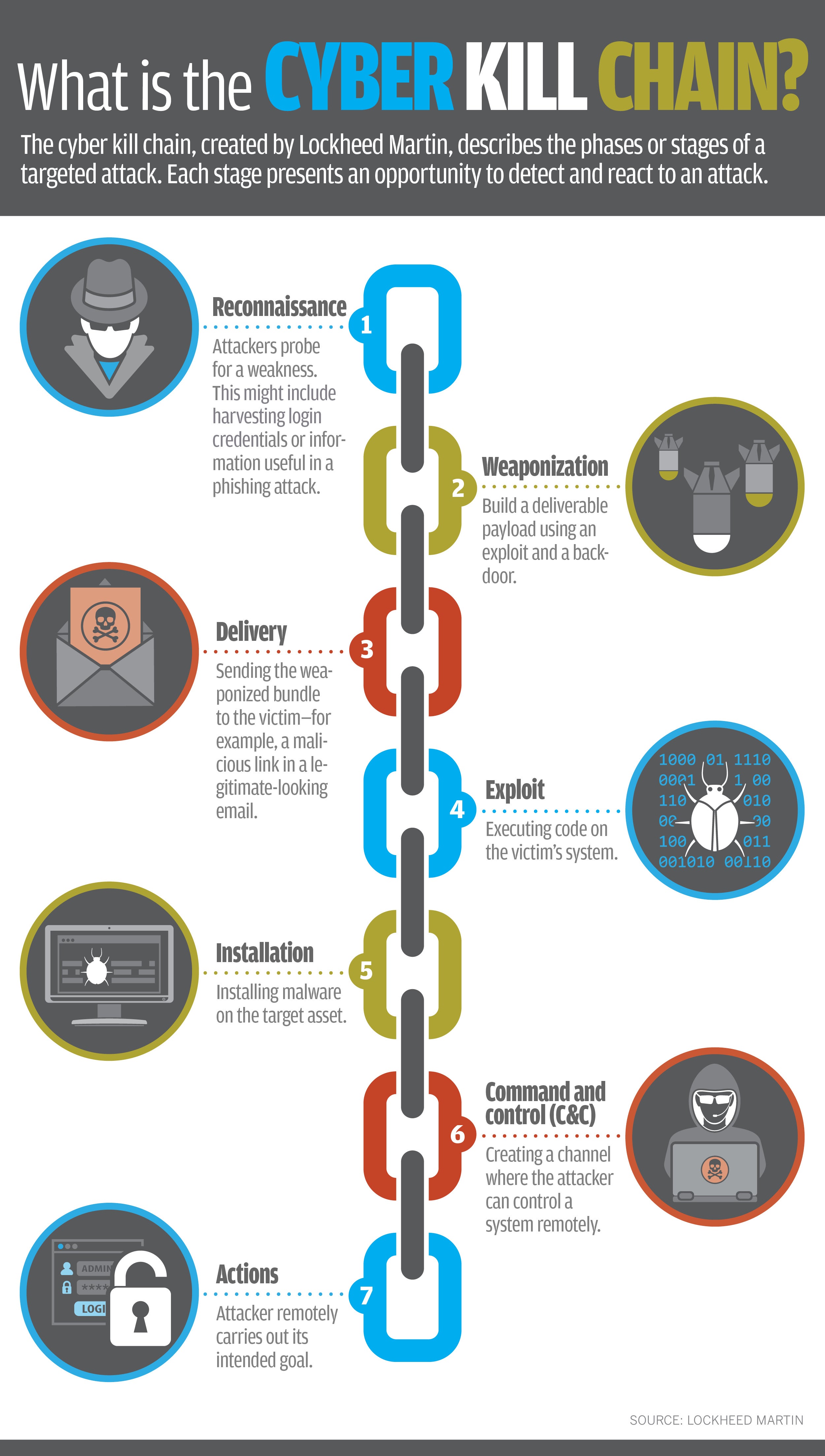
- Reconnaissance
- Weaponization
- Delivery
- Exploitation
- Installation
- Command and Control
- Actions on Objectives
Defenses Against Attacks; Five Fundamental Security Principles
- Layering: Multiple defense mechanisms.
- Limiting: Restricting access.
- Diversity: Using different security methods.
- Obscurity: Hiding system details.
- Simplicity: Easy internal use, complex externally.
Summary
Information security is a complex field facing constant evolution in attack methods and techniques. The core goal is protecting digital information through the CIA triad (Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability) and AAA (Authentication, Authorization, Accounting). Various actors, from financially motivated cybercriminals to state-sponsored attackers, pose threats. Attacks follow a structured process (the Cyber Kill Chain), and effective defenses rely on principles like layering, limiting access, diversity of methods, and obscuring system details while maintaining simplicity for internal users. The rise of connected devices and BYOD increases the challenges significantly.
