Table of Content
- Learning Objectives
- System Configuration - General - Boot - Services - Startup - Tools
- Change UAC Settings
- Computer Management
- System Information
- Resources Monitor
- Command Prompt
- Registry Editor
- Summary - Windows Fundamentals 2
- Conclusion
Learning Objectives
After completing this module, learners will be able to:
- Utilize the System Configuration utility (
msconfig) to manage startup options and services. - Modify User Account Control (UAC) settings to adjust system security levels.
- Effectively use Computer Management (
compmgmt.msc) to manage tasks, view events, administer users and groups, monitor performance, and manage storage and services. - Employ System Information (
msinfo32.exe) to gather comprehensive details about the system’s hardware, software, and configuration. - Leverage Resource Monitor (
resmon.exe) to analyze system resource usage (CPU, memory, disk, and network). - Employ essential command-line tools (
ipconfig,netstat,net, etc.) for system administration and troubleshooting. - Understand the purpose and structure of the Windows Registry and access it using Registry Editor (
regedit.exe). - Navigate the various sections within Computer Management and utilize its tools to perform system administration tasks.
System Configuration
The System Configuration utility (MSConfig) is for advanced troubleshooting, and its main purpose is to help diagnose startup issues.
There are several methods to launch System Configuration. One method is from the Start Menu.

NOTE
You need local administrator rights to open this utility.
The utility has five tabs across the top. Below are the names for each tab. We will briefly cover each tab in this task.
- General
- Boot
- Services
- Startup
- Tools
General
In the General tab, we can select what devices and services for Windows to load upon boot. The options are: Normal, Diagnostic, or Selective.

Boot
In the Boot tab, we can define various boot options for the Operating System.

Services
The Services tab lists all services configured for the system regardless of their state (running or stopped). A service is a special type of application that runs in the background.

Startup
In the Startup tab, you won’t see anything interesting in the attached VM. Below is a screenshot of the Startup tab for MSConfig from my local machine.

As you can see, Microsoft advises using Task Manager (taskmgr) to manage (enable/disable) startup items. The System Configuration utility is NOT a startup management program.
Tools
There is a list of various utilities (tools) in the Tools tab that we can run to configure the operating system further. There is a brief description of each tool to provide some insight into what the tool is for.

Questions
-
What is the name of the service that lists Systems Internals as the manufacturer?

- PsShutdown
-
Whom is the Windows license registered to?

- Windows User
-
What is the command for Windows Troubleshooting?
- C:\Windows\System32\control.exe /name Microsoft.Troubleshooting
-
What command will open the Control Panel? (The answer is the name of .exe, not the full path)
control.exe
Change UAC Settings
We’re continuing with Tools that are available through the System Configuration panel.
User Account Control (UAC) was covered in great detail in Windows Fundamentals 1 The UAC settings can be changed or even turned off entirely (not recommended).
You can move the slider to see how the setting will change the UAC settings and Microsoft’s stance on the setting.

Questions
- What is the command to open User Account Control Settings? (The answer is the name of the .exe file, not the full path)
UserAccountControlSettings.exe
Computer Management
We’re continuing with Tools that are available through the System Configuration panel.
The Computer Management (compmgmt) utility has three primary sections: System Tools, Storage, and Services and Applications.
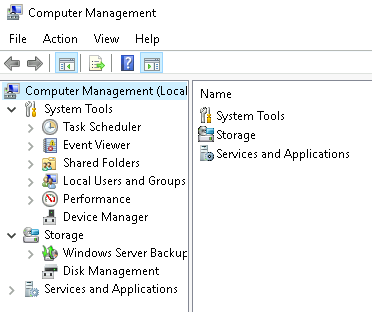
System Tools
Let’s start with Task Scheduler. Per Microsoft, with Task Scheduler, we can create and manage common tasks that our computer will carry out automatically at the times we specify.
A task can run an application, a script, etc., and tasks can be configured to run at any point. A task can run at log in or at log off. Tasks can also be configured to run on a specific schedule, for example, every five mins.
To create a basic task, click on Create Basic Task under Actions (right pane).

Next is Event Viewer.
Event Viewer allows us to view events that have occurred on the computer. These records of events can be seen as an audit trail that can be used to understand the activity of the computer system. This information is often used to diagnose problems and investigate actions executed on the system.

Event Viewer has three panes.
- The pane on the left provides a hierarchical tree listing of the event log providers. (as shown in the image above)
- The pane in the middle will display a general overview and summary of the events specific to a selected provider.
- The pane on the right is the actions pane.
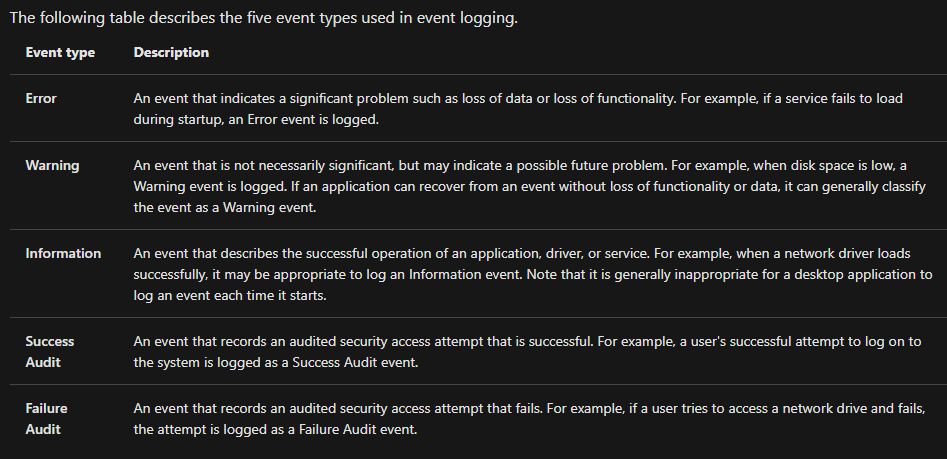
There are five types of events that can be logged. Below is a table from docs.microsoft.com providing a brief description for each.
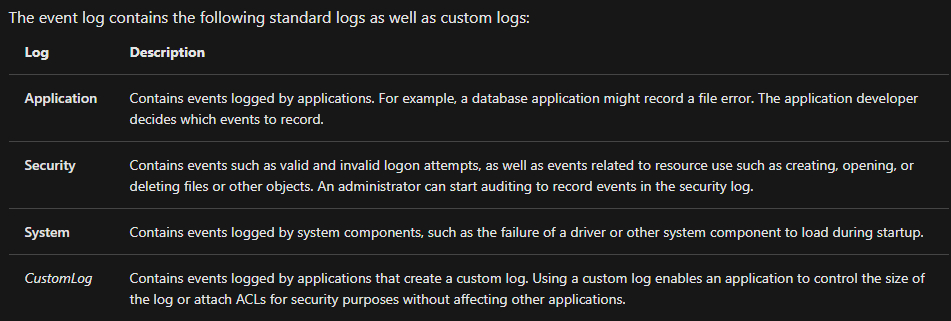
The standard logs are visible under Windows Logs. Below is a table from docs.microsoft.com providing a brief description for each.
For more information about Event Viewer and Event Logs, please refer to the Windows Event Log room.
Shared Folders is where you will see a complete list of shares and folders shared that others can connect to.

In the above image, under Shares, are the default share of Windows, C$, and default remote administration shares created by Windows, such as ADMIN$.
As with any object in Windows, you can right-click on a folder to view its properties, such as Permissions (who can access the shared resource).
Under Sessions, you will see a list of users who are currently connected to the shares. In this VM, you won’t see anybody connected to the shares.
All the folders and/or files that the connected users access will list under Open Files.
The Local Users and Groups section you should be familiar with from Windows Fundamentals 1 because it’s lusrmgr.msc.
In Performance, you’ll see a utility called Performance Monitor (perfmon).
Perfmon is used to view performance data either in real-time or from a log file. This utility is useful for troubleshooting performance issues on a computer system, whether local or remote.

Device Manager allows us to view and configure the hardware, such as disabling any hardware attached to the computer.

Storage
Under Storage is Windows Server Backup and Disk Management. We’ll only look at Disk Management in this room.
Note: Since the virtual machine is a Windows Server operating system, there are utilities available that you will typically not see in Windows 10.

Disk Management is a system utility in Windows that enables you to perform advanced storage tasks. Some tasks are:
- Set up a new drive
- Extend a partition
- Shrink a partition
- Assign or change a drive letter (ex. E:)
Services and Applications

Recall from the previous task; a service is a special type of application that runs in the background. Here you can do more than enable and disable a service, such as view the Properties for the service.
WMI Control configures and controls the Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) service.
Per Wikipedia, “WMI allows scripting languages (such as VBScript or Windows PowerShell) to manage Microsoft Windows personal computers and servers, both locally and remotely. Microsoft also provides a command-line interface to WMI called Windows Management Instrumentation Command-line (WMIC).”
Note: The WMIC tool is deprecated in Windows 10, version 21H1. Windows PowerShell supersedes this tool for WMI.
Questions
- What is the command to open Computer Management? (The answer is the name of the .msc file, not the full path)
compmgmt.msc
- At what time every day is the GoogleUpdateTaskMachineUA task configured to run?
6:15 AM
- What is the name of the hidden folder that is shared?
sh4r3dF0Ld3r
System Information
We’re continuing with Tools that are available through the System Configuration panel.
What is the System Information (msinfo32) tool?
Per Microsoft, “Windows includes a tool called Microsoft System Information (Msinfo32.exe). This tool gathers information about your computer and displays a comprehensive view of your hardware, system components, and software environment, which you can use to diagnose computer issues.”
The information in System Summary is divided into three sections:
- Hardware Resources
- Components
- Software Environment
System Summary will display general technical specifications for the computer, such as processor brand and model.

The information displayed in Hardware Resources is not for the average computer user. If you want to learn more about this section, refer to the official Microsoft page.

Under Components, you can see specific information about the hardware devices installed on the computer. Some sections don’t show any information, but some sections do, such as Display and Input.

In the Software Environment section, you can see information about software baked into the operating system and software you have installed. Other details are visible in this section as well, such as the Environment Variables and Network Connections.

Recall from the Windows Fundamentals 1 (The Windows\System32 Folder task) where Environment Variables was briefly touched on.
Per Microsoft, “Environment variables store information about the operating system environment. This information includes details such as the operating system path, the number of processors used by the operating system, and the location of temporary folders.
The environment variables store data that is used by the operating system and other programs. For example, the WINDIR environment variable contains the location of the Windows installation directory. Programs can query the value of this variable to determine where Windows operating system files are located”.
Click on Environment Variables to see the assigned values for the virtual machine.

Another method to view environment variables is Control Panel > System and Security > System > Advanced system settings > Environment Variables OR Settings > System > About > system info > Advanced system settings > Environment Variables.

The detour is over. Let’s redirect our attention back to msinfo32 and pick up where we left off.
Towards the very bottom of this utility, there is a search bar. Please give it a go. Select Components and search for IP address.

Questions
- What is the command to open System Information? (The answer is the name of the .exe file, not the full path)
- msinfo32.exe
- What is listed under System Name?
- THM-WINFUN2
- Under Environment Variables, what is the value for ComSpec?
- %SystemRoot%\system32\cmd.exe
Resources Monitor
We’re continuing with Tools that are available through the System Configuration panel.
What is Resource Monitor (resmon)?
Per Microsoft, “Resource Monitor displays per-process and aggregate CPU, memory, disk, and network usage information, in addition to providing details about which processes are using individual file handles and modules. Advanced filtering allows users to isolate the data related to one or more processes (either applications or services), start, stop, pause, and resume services, and close unresponsive applications from the user interface. It also includes a process analysis feature that can help identify deadlocked processes and file locking conflicts so that the user can attempt to resolve the conflict instead of closing an application and potentially losing data.”
As some of the other tools mentioned in this room, this utility is geared primarily to advanced users who need to perform advanced troubleshooting on the computer system.
In the Overview tab, Resmon has four sections:
- CPU
- Disk
- Network
- Memory

The same four sections have corresponding tabs across the top. See below.

Note that each tab has additional information for each. An image is shown below for each tab.
CPU

Memory

Disk

Network

Although not captured in any of the images above, Resource Monitor has a pane at the far right. This pane shows a graphical view in real-time for each section.
Note: The information displayed in Resource Monitor will be different for you compared to the images above.
Questions
- What is the command to open Resource Monitor? (The answer is the name of the .exe file, not the full path)
resmon.exe
Command Prompt
We’re continuing with Tools that are available through the System Configuration panel.
The command prompt (cmd) can seem daunting at first, but it’s really not that bad once you understand how to interact with it.
In early operating systems, the command line was the sole way to interact with the operating system.
When the GUI (graphical user interface) was introduced, it allowed users to perform complex tasks with a few clicks of a button instead of entering commands in the command prompt.
Even though the GUI is the primary way to interact with the operating system, a computer user can still interact via the command prompt.
In this task, we’ll only cover a few commands that a computer user can run in the command prompt to obtain information about the computer system.
Let’s start with a few simple commands, such as hostname and whoami.
The command hostname will output the computer name.

The command whoami will output the name of the logged-in user.

Next, let’s look at some commands that are useful when troubleshooting.
A command used often is ipconfig. This command will show the network address settings for the computer.

Each command will have a help manual to explain the expected syntax to execute the command properly, along with any additional parameters that can be added to the command to expand its execution.
A command to retrieve the help manual for a command is /?.
For example, to see the help manual for ipconfig, you can use the following command: ipconfig /?

Note: To clear the command prompt screen, the command is cls.
The next command is netstat. Per the help manual, this command will display protocol statistics and current TCP/IP network connections.

In the above image, the line within the red box shows us an example syntax for the command.
The structure tells us the netstat command can be run alone or with parameters, such as -a, -b, -e, etc.
When any of the parameters are appended to the root command, netstat in this case, the output changes. Play with a few to see for yourself.
The net command is primarily used to manage network resources. This command supports sub-commands.
If you type net without a sub-command, the output will show the syntax for the root command showing a few of the sub-commands you can use.

For the net command, to display the help manual /? will not work. In this case, you need to use different syntax, which is net help.

So, if you wish to see the help information for net user , the command is net help user.

You can use the same command to view the help information for other useful net sub-commands, such as localgroup, use, share, and session.
Refer to the following link to see a comprehensive list of commands you can execute in the command prompt here.
Questions
- In System Configuration, what is the full command for Internet Protocol Configuration?
- C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe /k %windir%\system32\ipconfig.exe
- For the ipconfig command, how do you show detailed information?
- ipconfig /all
Registry Editor
We’re continuing with Tools that are available through the System Configuration panel.
The Windows Registry (per Microsoft) is a central hierarchical database used to store information necessary to configure the system for one or more users, applications, and hardware devices.
The registry contains information that Windows continually references during operation, such as:
- Profiles for each user
- Applications installed on the computer and the types of documents that each can create
- Property sheet settings for folders and application icons
- What hardware exists on the system
- The ports that are being used.
Warning: The registry is for advanced computer users. Making changes to the registry can affect normal computer operations.
There are various ways to view/edit the registry. One way is to use the Registry Editor (regedit).

Refer to the following Microsoft documentation here to learn more about the Windows Registry.
Questions
- What is the command to open the Registry Editor? (The answer is the name of the .exe file, not the full path)
regedt32.exe
Summary - Windows Fundamentals 2
This room covers advanced Windows system tools, building on the basics from Windows Fundamentals 1.
I. System Configuration (msconfig): Used for troubleshooting startup issues. Tabs include: General (boot options), Boot (OS boot settings), Services (background processes), Startup (use Task Manager instead), and Tools (access to other utilities).
II. UAC Settings: Modifiable via UserAccountControlSettings.exe. Adjusts the level of User Account Control.
III. Computer Management (compmgmt.msc): Provides access to: System Tools: Task Scheduler (scheduling automated tasks), Event Viewer (viewing system events – five types detailed in original document, standard logs detailed in original document), Shared Folders (managing network shares), Local Users and Groups (lusrmgr.msc), Performance Monitor (perfmon), Device Manager. Storage: Disk Management (managing disks and partitions).
- Services and Applications: Managing services (background processes), WMI Control.
IV. System Information (msinfo32.exe): Displays comprehensive system information (hardware, software, environment variables).
V. Resource Monitor (resmon.exe): Provides real-time monitoring of CPU, memory, disk, and network usage.
VI. Command Prompt (cmd): Essential commands covered: hostname, whoami, ipconfig (including /all), netstat, net (with subcommands like user, localgroup, etc.), cls.
VII. Registry Editor (regedit.exe or regedt32.exe): For advanced users; allows viewing and editing the Windows Registry (use caution!).
This summary covers all key tools and concepts from the room. Refer to the original document for detailed explanations and screenshots.
Conclusion
This TryHackMe room built upon the foundation established in “Windows Fundamentals 1,” delving into advanced system configuration tools and utilities accessible through System Configuration. We explored msconfig and its various tabs, learned how to modify UAC settings, and extensively examined the capabilities of Computer Management, including Task Scheduler, Event Viewer, Shared Folders, Local Users and Groups, Performance Monitor, and Device Manager. The room also covered System Information (msinfo32), Resource Monitor (resmon), and essential command-line tools like ipconfig, netstat, and net, concluding with an introduction to the Windows Registry and its editor, regedit. This room equips learners with practical skills to troubleshoot, configure, and monitor Windows systems at a more advanced level.